2.1. Build a Demo ParallelCluster#
Step by Step Instructions to Build a Demo ParallelCluster.
Establish Identity and Permissions
AWS Identity and Access Management Roles Requires the user to have AWS Identity and Access Management roles in AWS ParallelCluster
AWS ParallelCluster uses multiple AWS services to deploy and operate a cluster. See the complete list in the AWS Services used in AWS ParallelCluster section. It appears you can create the demo cluster, and even the intermediate or advanced cluster, but you can’t submit a slurm job and have it provision compute nodes until you have the IAM Policies set for your account. This likely requires the system administrator who has permissions to access the AWS Web Interface with root access to add these policies and then to attach them to each user account.
Use the AWS Web Interface to add a policy called AWSEC2SpotServiceRolePolicy to the account prior to running a job that uses spot pricing on the ParallelCluster.
2.1.1. Install Parallel Cluster AWS CLI 3.0#
Use Parallel Cluster AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) v3.0 to configure and launch a demo cluster
Requires the user to have a key.pair that was created on an ec2.instance
See also
Install AWS ParallelCluster Command Line Interface on your local machine
Create a virtual environment on a linux machine to install aws-parallel cluster
python3 -m virtualenv ~/apc-ve
source ~/apc-ve/bin/activate
python --version
python3 -m pip install --upgrade aws-parallelcluster
pcluster version
Install node.js
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.38.0/install.sh
chmod ug+x ~/.nvm/nvm.sh
source ~/.nvm/nvm.sh
nvm install node
node --version
Verify that AWS ParallelCluster is installed on local machine
Run pcluster version.
pcluster version
Output:
{
"version": "3.1.2"
}
Note
If you start a new terminal window, you need to re-activate the virtual environment using the following commands:
source ~/apc-ve/bin/activate
source ~/.nvm/nvm.sh
Verify that the parallel cluster is working using:
pcluster version
Configure AWS Command line credentials on your local machine
aws configure
2.1.2. Configure a Demo Cluster#
To create a parallel cluster, a yaml file needs to be created that is unique to your account.
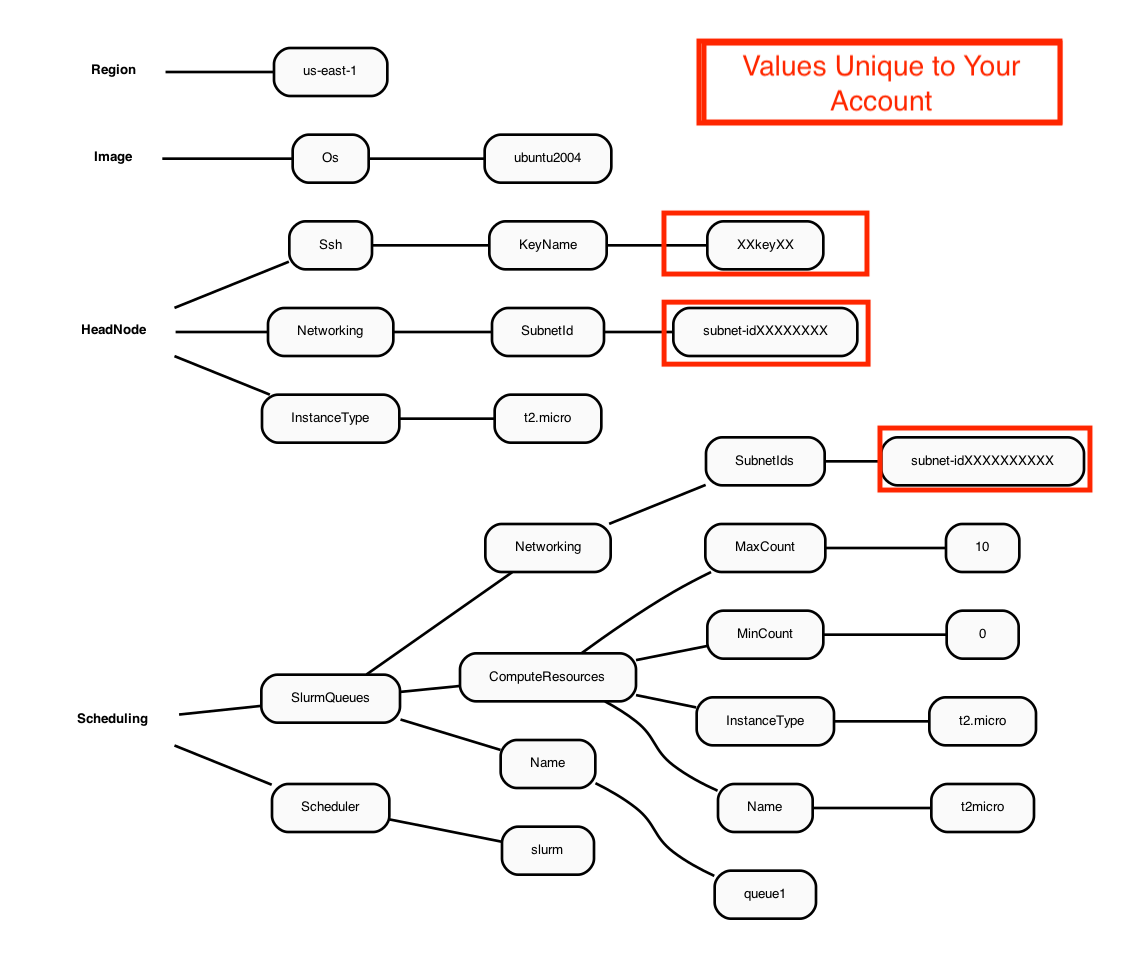
An example of the yaml file contents is described in the following Diagram:
Figure 1. Diagram of YAML file used to configure a ParallelCluster with a t2.micro head node and t2.micro compute nodes
See also
Create a yaml configuration file for the cluster following these instructions
pcluster configure --config new-hello-world.yaml
Input the following answers at each prompt:
Allowed values for AWS Region ID:
us-east-1Allowed values for EC2 Key Pair Name:
choose your key pairAllowed values for Scheduler:
slurmAllowed values for Operating System:
ubuntu2004Head node instance type:
t2.microNumber of queues:
1Name of queue 1:
queue1Number of compute resources for queue1 [1]:
1Compute instance type for compute resource 1 in queue1:
t2.microMaximum instance count [10]:
10Automate VPC creation?:
yAllowed values for Availability Zone:
1Allowed values for Network Configuration:
2. Head node and compute fleet in the same public subnet
Beginning VPC creation. Please do not leave the terminal until the creation is finalized
Note
The choice of operating system (specified during the yaml creation, or in an existing yaml file) determines what modules and gcc compiler versions are available.
Centos7 has an older gcc version 4
Ubuntu2004 has gcc version 9+
Alinux or Amazon Linux/Red Hat Linux (haven’t tried)
Examine the yaml file
cat new-hello-world.yaml
Region: us-east-1
Image:
Os: ubuntu2004
HeadNode:
InstanceType: t2.micro
Networking:
SubnetId: subnet-xx-xx-xx <<< unique to your account
Ssh:
KeyName: your-key <<< unique to your account
Scheduling:
Scheduler: slurm
SlurmQueues:
- Name: queue1
ComputeResources:
- Name: t2micro
InstanceType: t2.micro
MinCount: 0
MaxCount: 10
Networking:
SubnetIds:
- subnet-xx-xx-xx <<< unique to your account
Note
The above yaml file is the very simplest form available. If you upgrade the compute node to using a faster compute instance, then you will need to add additional configuration options (networking, elastic fabric adapter) to the yaml file. These modifications will be highlighted in the yaml figures provided in the tutorial.
The key pair and Subnetid in the yaml file are unique to your account. To create the AWS Intermediate ParallelCluster, the key pair and subnet ID from the new-hello-world.yaml file that you created using your account will need to be transferred to the Yaml files that will be used to create the Intermediate ParallelCluster in the next section of the tutorial. You will need to edit these yaml files to use the key pair and your Subnetid that are valid for your AWS Account.
2.1.3. Create a Demo Cluster#
pcluster create-cluster --cluster-configuration new-hello-world.yaml --cluster-name hello-pcluster --region us-east-1
Check on the status of the cluster
pcluster describe-cluster --region=us-east-1 --cluster-name hello-pcluster
List available clusters
pcluster list-clusters --region=us-east-1
Check on status of cluster again
pcluster describe-cluster --region=us-east-1 --cluster-name hello-pcluster
After 5-10 minutes, you see the following status: “clusterStatus”: “CREATE_COMPLETE”
While the cluster has been created, only the t2.micro head node is running. Before any jobs can be submitted to the slurm queue, the compute nodes need to be started.
Note
The compute nodes are not “provisioned” or “created” at this time (so they do not begin to incur costs). The compute nodes are only provisioned when a slurm job is scheduled. After a slurm job is completed, then the compute nodes will be terminated after 5 minutes of idletime.
2.1.4. Login to the ParallelCluster#
Note
replace the your-key.pem key pair with your key pair you will need to change the permissions on your key pair so to be read only by owner.
cd ~
chmod 400 your-key.pem
Example: pcluster ssh -v -Y -i ~/your-key.pem –cluster-name hello-pcluster
pcluster ssh -v -Y -i ~/[your-key-pair] --cluster-name hello-pcluster
login prompt should look something like (this will depend on what OS was chosen in the yaml file).
[ip-xx-x-xx-xxx pcluster-cmaq]
Check what modules are available on the ParallelCluster
module avail
Check what version of the compiler is available
gcc --version
Need a minimum of gcc 8+ for CMAQ
Check what version of openmpi is available
mpirun --version
Need a minimum openmpi version 4.0.1 for CMAQ
Verify that Slurm is available (if slurm is not available, then you may need to try a different OS)
which sbatch
Do not install sofware on this demo cluster
the t2.micro head node is too small
Save the key pair and SubnetId from this new-hello-world.yaml to use in the yaml for the Intermediate Tutorial
2.1.5. Exit the cluster#
exit
2.1.6. Delete the Demo Cluster#
pcluster delete-cluster --cluster-name hello-pcluster --region us-east-1
See also
pcluster --help